
There’s more to say about this topic, but I’ll save that for an in-depth tutorial. The give-take relationship between the front-end and the back-end is called the Client-Server model. Your location relative to the web page’s location (where it’s hosted) also affects both the request-response time, and page loading time. The laptop used to be able to connect to the server, but all of a sudden it no longer can, yet the desktop can still connect to the server. The communication is unidirectional: The client issues a request to the server, and after processing the request the server returns a response. These two components interact with each other through a network connection using a given protocol.
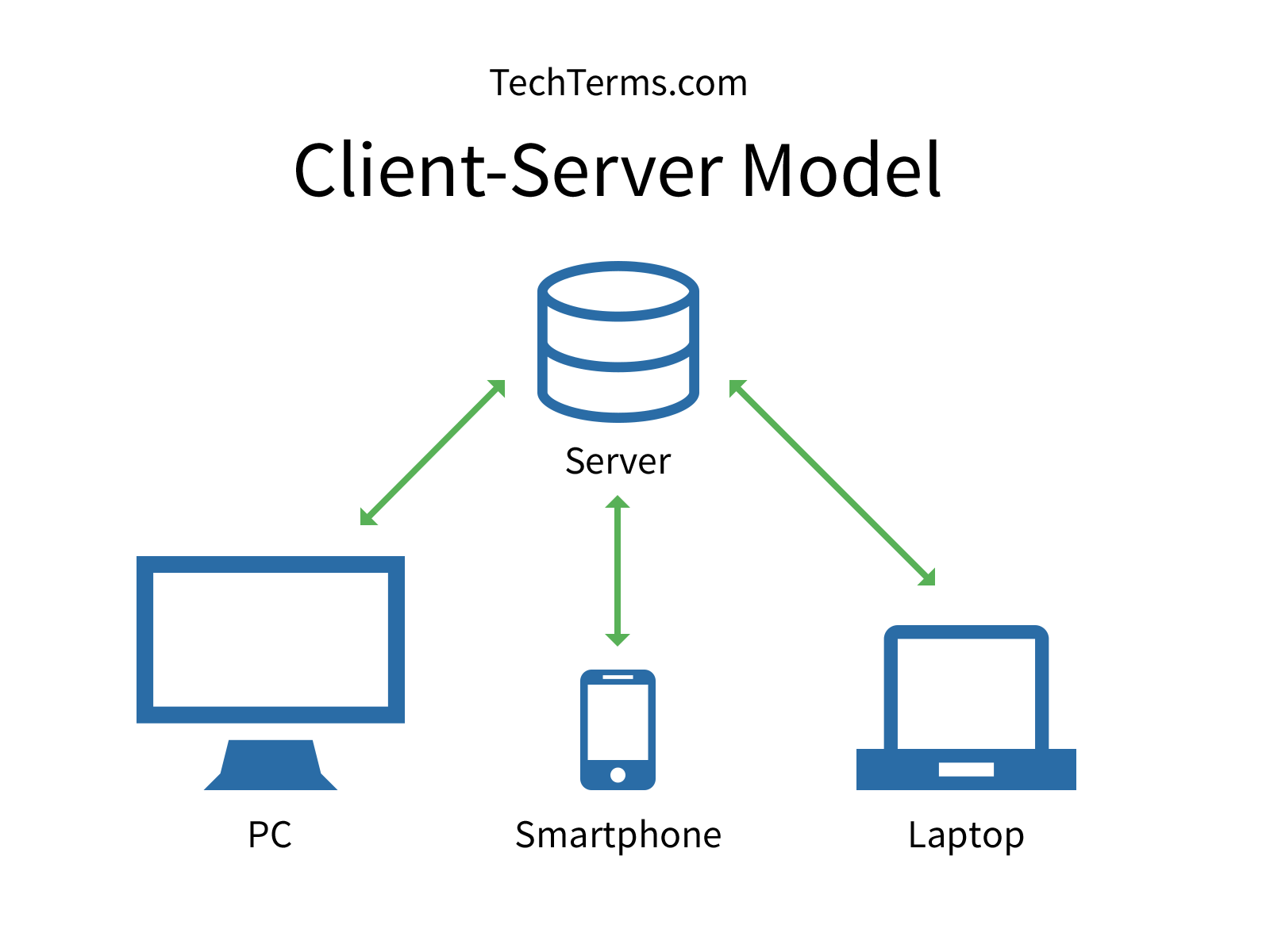
The more data the web page has (especially images and videos) the longer it takes to load. Wireless clients cant connect to wired client So I have a server connected to the router via Ethernet, a laptop connected through WiFi, and a desktop also connected through Ethernet. As depicted in Figure 2.12, the client/server model features two major components: a server and a client. The request process takes place in a matter of milliseconds but it can take anywhere from 100ms or less to several seconds before you can see the entire web page in your browser window. INTRODUCTIONA network is an interconnection ofcomputers may be wired or wireless fordata communication, remote accessing,resource management and data sharing. If the web server (the guard) accepts your request, it will try to fetch the web page you want to see from the database, and send you the necessary files to display the site (HTML, CSS, JavaScript, images, video). To get anything displayed in your browser, your client (your web browser) first sends a request to the web server of the site you want to visit (it happens behind the scenes). The most basic example of a request is when you go to any website either via your address bar or by clicking on a hyperlink. To get access to any web content, we first need to ask for permission from the guard, aka web server. For example, Instagram, Twitter, or any app where you can sign in/ sign out, stream video, upload files, and write messages.Īs you can see in the illustration above, to either send or receive information from the database, we need to go through a so-called web server when we make requests on the client.Ī web server is like a guard that protects your precious file storage facility (database) from intruders.

Otherwise, we won’t be able to manipulate data (text, images, videos) back and forth, which is crucial on most platforms. For example: web servers store and maintain web content, which is downloaded upon request to client computers mail servers handle. Your client (front-end) and server (back-end) must be able to communicate with each other. The internet largely works on the client-server model. A quick introduction to the give/take relationship between the front-end and the back-end, often referred to as the Client-Server model.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
